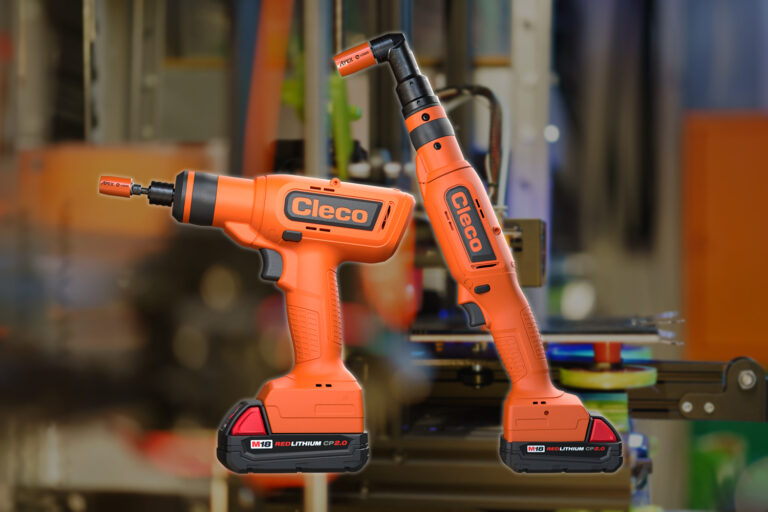
In the world of research and product development, the ability to rapidly iterate is everything. Whether you’re designing a new piece of industrial machinery, a medical device, or a lightweight aerospace component, success in the lab is measured by your ability to move fast without compromising precision. That’s where Cleco’s CellClutch Cordless Electric Tools come into play.
Originally engineered for high-volume production environments, the CellClutch platform has become an essential tool in engineering, prototyping, and R&D labs – places where the future of manufacturing is born. These environments demand torque accuracy, flexibility, ease of reprogramming, and clean, cordless operation. And unlike traditional torque tools that are either overbuilt for fixed jobs or under-equipped for nuanced applications, the CellClutch is perfectly balanced for exploratory, fast-paced build environments.
Why Prototyping Environments Are Different
Prototyping and R&D labs differ from production lines in key ways:
- High variation in parts and assembly processes
- Frequent design changes requiring tool adaptability
- Smaller batch sizes or one-off builds
- No fixed stations or integrated production systems
- Focus on learning and iteration, not just output
- Need for documentation to trace results, especially in regulated industries
In these settings, engineers and technicians must test configurations, validate tolerances, and repeat tasks reliably—all while balancing creativity with technical control. That’s exactly what CellClutch enables.
- Cordless mobility: No air lines or tethered power—ideal for clutter-free benches
- Programmable torque ranges: Ideal for working across fastener sizes and materials
- Multi-stage rundown: Enables soft starts, angle control, and layered torque strategies
- Torque repeatability: ±10% tolerance, CMK > 1.67 — perfect for controlled experiments
- LED pass/fail indicators: Real-time feedback for validation during development
- Data logging (Connect models): Capture and analyze torque/angle for each fastener
- Quick reprogramming: Switch tasks or iterate builds with no external setup tools
- Right-angle and pistol configurations: Adapt to tight spots or complex geometries
- Milwaukee M18 battery compatibility: Shared ecosystem, reliable power
Together, these features offer precision and flexibility—qualities that align with the goals of any experimental or pre-production build.
Use Cases in Research & Prototyping Labs
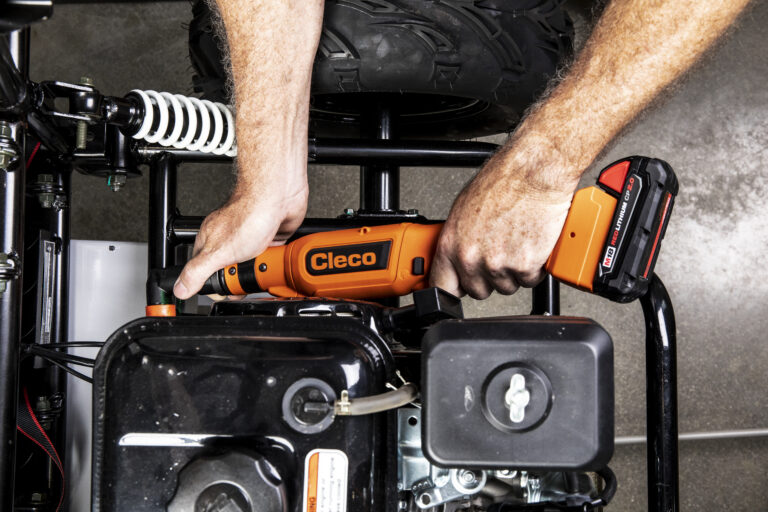

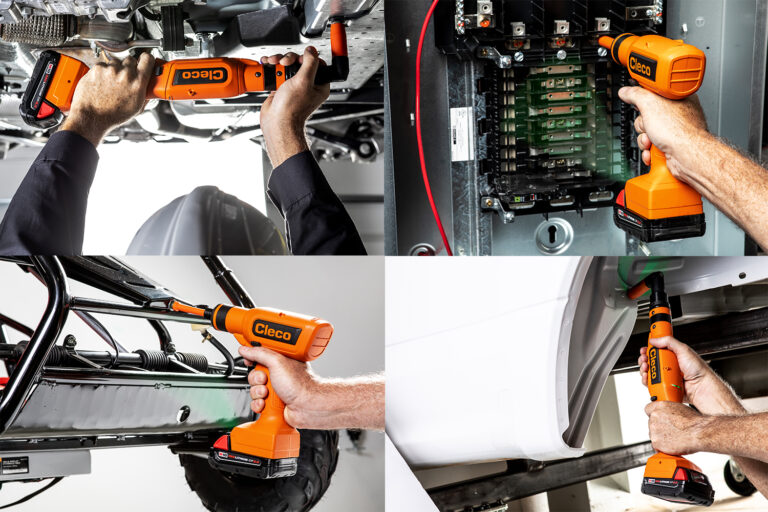
1. Prototype Frame Assembly
Whether you’re designing a new vehicle chassis, drone housing, or robotic structure, fastening the mechanical frame is often the first and most frequent task in any build cycle. It also often involves repetitive assembly and disassembly for fit testing or material evaluation.
CellClutch tools support this by:
- Offering multiple torque profiles so that the same tool can handle fasteners across various materials (e.g., steel to carbon fiber, aluminum to plastic)
- Cordless operation, allowing movement between stations, jigs, or test cells
- Fast reconfiguration, reducing downtime during iteration
Right Angle models allow work inside tight frames and enclosures, while Pistol Grip variants excel for flat or vertical surfaces.
2. Fastener Testing & Validation
Labs often run torque studies to determine optimal fastener types, preload levels, or material compatibility. These may include:
- Comparative testing between thread types or finishes
- Validation of gasket compression via controlled torque application
- Studying effects of thermal expansion on fastened joints
Cleco’s torque repeatability and data-logging capabilities make it ideal for capturing consistent, measurable fastening results. Researchers can export logs, validate CMK values, and integrate torque data into test reports or engineering evaluations.
3. Electronics & Control Module Development
In mechatronics and hardware R&D, engineers frequently install and remove PCBs, sensors, and enclosures. These parts are extremely sensitive to torque, often requiring delicate, multi-stage tightening to avoid PCB flex or cracking.
Cleco’s advantages here include:
- Low torque range (starting around 1.6 ft-lb or ~2.2 Nm)
- Visual and audible feedback for validation during install
- Multi-stage rundown capability, useful for layered assemblies or seating operations
- No back-torque, reducing the risk of damaging internal components
This makes the tool equally suitable for both product assembly and test-rig construction involving electronics.
4. Medical Device Prototyping
Medical technology developers use CellClutch tools for:
- Implant system casing assembly
- Handheld diagnostic device fastening
- Prototyping orthopedic surgical tools or instruments
These applications require precise torque control to avoid micro-fractures in polymers or interference with internal mechanics. Cleco’s clean, low-vibration cordless design is perfect for labs that simulate cleanroom conditions or require safe, contamination-free tool performance.
5. Build Fixtures, Test Beds, and Mockups
Engineering teams frequently build:
- Test beds for dynamic validation
- Mockups for customer feedback
- Demonstrators for trade shows or internal presentations
These tasks often involve a combination of structural fastening and cosmetic detailing. With CellClutch:
- One tool handles it all with tool-less program switching
- Build teams can move quickly across bench and floor-level work
- Quality feedback via LEDs ensures consistent presentation builds
- Traceability data supports internal sign-offs or design freeze audits
Data, Compliance, and Repeatability

In regulated industries—such as aerospace, medical devices, or automotive – prototype-level traceability is increasingly required to validate design intent and process development. CellClutch Connect tools meet this need by:
- Storing torque/angle data per fastener
- Linking data to operator ID or part serial number
- Connecting to mPro controllers or MES systems via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth
- Supporting batch tracking for design verification records
This makes Cleco tools an important link in the digital thread of design validation, ensuring a smooth transition from lab to production.
Ergonomics and Daily Use in the Lab
Prototyping often involves repetitive manual tasks, so operator comfort is essential. Cleco tools help reduce strain and increase accuracy with:
- Low reaction force from mechanical clutch shutoff
- Well-balanced design that reduces wrist fatigue
- Cordless use, eliminating trip hazards or cluttered workspaces
- Single-hand operation, useful when securing parts or holding components
Engineers can focus on problem-solving instead of managing tool limitations.
Bridging the Gap Between Engineering and Production
Perhaps one of CellClutch’s greatest strengths in the lab is its alignment with production tooling standards. By using Cleco tools during the prototyping and pilot build phase, engineers can:
- Develop torque specs based on production tool performance
- Train operators and write work instructions that carry directly into manufacturing
- Validate assembly sequences and capture repeatable process metrics
- Reduce transition time from pilot line to full-scale assembly
This ensures consistency from R&D to production—accelerating time-to-market and reducing product launch risk.
Conclusion
In research and prototyping labs, precision and agility aren’t trade-offs—they’re necessities. Whether you’re inventing the next generation of medical technology, fine-tuning robotic arms, or pressure-testing your newest industrial product, the Cleco CellClutch Cordless Tool System delivers unmatched value.
By combining torque control, data intelligence, and ergonomic freedom, CellClutch tools help labs build faster, smarter, and more accurately. With every iteration, every prototype, and every idea tested, these tools provide the foundation for innovation—helping engineers bring new possibilities into the world, one perfectly torqued fastener at a time.

